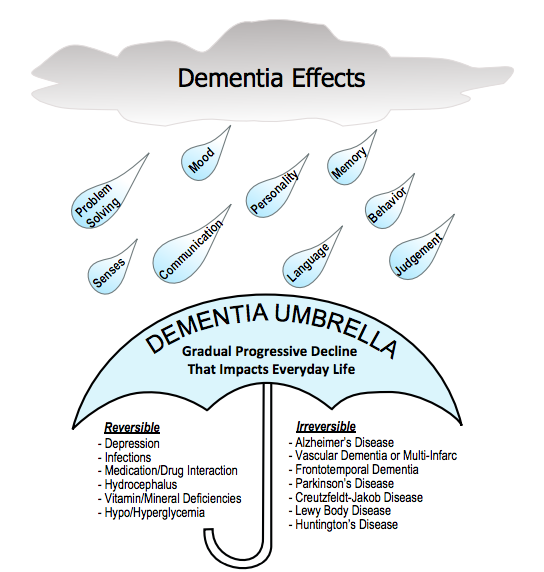
Dementia is an umbrella term that describes a group of symptoms affecting memory, thinking, and social abilities severely enough to interfere with daily functioning. Dementia in itself is not a specific disease but instead is the symptom of a disease.
There are many conditions that can result in symptoms of dementia. Some dementia is reversible. In this case, dementia is caused by a condition that is treatable. When the underlying problem causing dementia symptoms is identified and treated, the dementia symptoms often clear.
Reversible Dementia Causes
Reversible conditions include:
- Depression
- Infection
- Medication side effects
- Vitamin/mineral deficiencies
- Dehydration
- Thyroid problems
- Hydrocephalus
- Hypo/Hyperglycemia
- Delirium
Irreversible Dementia Types
Irreversible dementia occurs when a disease results in permanent brain damage. Some of the more common irreversible causes of dementia include:
Alzheimer's disease, the most common, is a progressive brain disease that damages brain cells. Brain changes lead to growing trouble with memory, thinking and reasoning, judgement, performing familiar tasks, changes in personality and behavior, and decreased physical function.
Vascular dementia caused by brain damage from impaired blood flow, such as stroke. Symptoms vary depending on the part of the brain where blood flow is impaired. Symptoms often follow a more stepwise deterioration followed by a period of relative recovery.
Frontotemporal dementia is a progressive condition which predominantly affects behavior and personality. Lewy body dementia causes a progressive decline in mental abilities. Visual hallucinations and Parkinson's disease-like symptoms such as rigid muscles, slow movement and tremors are common.
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive disorder of the nervous system that affects movement. 50-80 percent develops dementia as their disease progresses.
Dementia, whether it is reversible or irreversible is a loss of mental function that can affect language, memory, visual and spatial abilities, or judgment.